 |
trigo table |
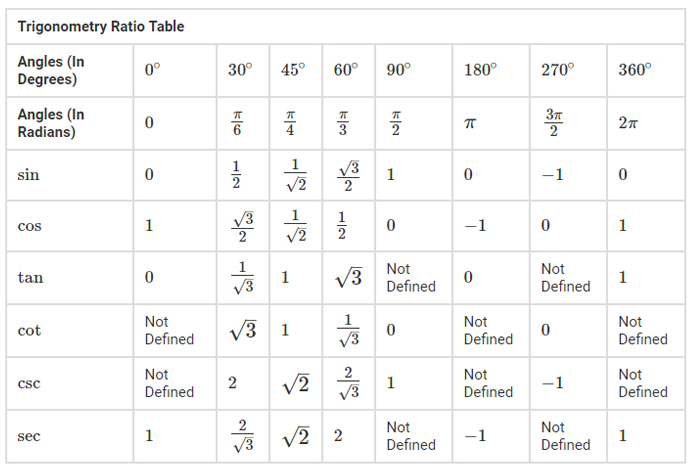
Trigonometry Table: Trigonometry is a branch of Mathematics that deals with the study of length, angles, and their relationships in a triangle. Trigonometric ratios are applicable only for right angle triangles, with one of the angles is equal to 90o
Trigonometry Table
The trig table is made up of the following trigonometric ratios that are interrelated to each other – sin, cos, tan, cos, sec, cot.
sin (reciprocal of cosecant) = opposite over hypotenuse
cos (reciprocal of secant) = adjacent over hypotenuse
tan (reciprocal of cotangent) = opposite over adjacent
cot (reciprocal of tangent) = adjacent over opposite
cosec (reciprocal of sine) = hypotenuse over opposite
sec (reciprocal of cosine) = hypotenuse over adjacent
The calculations can easily be figured out by memorizing a table of functions most commonly known as the Trigonometric Table. This finds use in several areas. Some of them include navigation video games, aviation, science, geography, engineering, geometry, etc. The trigonometric table helped in many developments and in the field of Mechanical Engineering for the first innovation.
The Trig ratios table gives us the values of standard trigonometric angles such as 0°, 30°, 45°, 60°, and 90°. These values hold increased precedence as compared to others as the most important problems employ these ratios. It is therefore very important to know and remember the ratios of these standard angles.
Remembering the trigonometry table will be useful as it finds many applications, and there are many methods to remember the table. Knowing the Trigonometry formulas, ratios and identities automatically will lead to figuring out the table and the values. The Trigonometric ratio table is dependent upon the trigonometry formulas in the same way all the functions of trigonometry are interlinked with each other.
Before attempting to begin, it is better to try and remember these values and know the following trigonometric ratios of complementary angles.
sin x = cos (90∘−x)
cos x = sin (90∘−x)
tan x = cot (90∘−x)
cot x = tan (90∘−x)
sec x = cot (90∘−x)
cot x = sec (90∘−x)
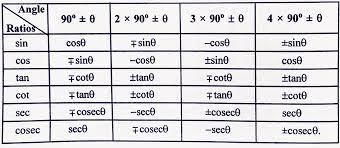
Reciprocal Relations of Trigonometric Ratios
1 / sin x = cosec x
1 / cos x= sec x
1 / sec x= cos x
1 / tan x= cot x
1 / cot x= tan x
1/ cosec x = sin x
Now let us discuss different values
For sin
For memorising sin 0°, sin 30°, sin 45°, sin 60° and sin 90°
We should learn it like
sin 0° = 0
sin 30° = 1/2
sin 45° = 1/√2
sin 60° = √3/2
sin 90° = 1
So, our pattern will be like
0, 1/2, 1/√2, √3/2, 1
For cos
For memorising cos 0°, cos 30°, cos 45°, cos 60° and cos 90°
Cos is the opposite of sin.
We should learn it like
cos 0° = sin 90° = 1
cos 30° = sin 60° = √3/2
cos 45° = sin 45° = 1/√2
cos 60° = sin 30° = 1/2
cos 90° = sin 0° = 0
So, for cos, it will be like
1, √3/2, 1/√2, 1/2, 0
For tan
We know that tan θ = sin θ /cos θ
So, it will be
tan 0° = sin 0° / cos 0° = 0/1 = 0
tan 30° = sin 30° / cos 30° = (1/2)/ (√3/2) = 1/√3
tan 45° = sin 45° / cos 45° = (1/√2)/ (1/√2) = 1
tan 60° = sin 60° / cos 60° = (√3/2) / (1/2) = √3
tan 90° = sin 90° / cos 90° = 1/0 = Not Defined = ∞
So, for tan, it is
0, 1/√3, 1, √3, ∞
For cosec
We know that
cosec θ = 1/sin θ
For sin, we know
0, 1/2, 1/√2, √3/2, 1
So, for Cosec it will be
cosec 0° = 1 / sin 0° = 1/0 = Not Defined = ∞
cosec 30° = 1 / sin 40° = 1/(1/2) = 2
cosec 45° = 1 / sin 45° = 1/(1/√2) = √2
cosec 60° = 1 / sin 60° = 1/(√3/2) = 2/√3
cosec 90° = 1 / sin 90° = 1/1 = 1
So, for Cosec, it is
∞, 2, √2, 2/√3, 1
For sec
We know that
sec θ = 1/cos θ
For cos, we know
1, √3/2, 1/√2, 1/2, 0
So, for a sec it will be
sec 0° = 1 / cos 0° = 1/1 = 1
sec 30° = 1 / cos 40° = 1/(√3/2) = 2/√3
sec 45° = 1 / cos 45° = 1/(1/√2) = √2
sec 60° = 1 / cos 60° = 1/(1/2) = 2
sec 90° = 1 / cos 90° = 1/0 = Not Defined = ∞
So, for a sec, it is
1, 2/√3, √2, 2, ∞
For cot
We know that
cot θ = 1/tan θ
For tan, we know that
0, 1/√3, 1, √3, ∞
So, for a cot, it will be
cot 0° = 1 / tan 0° = 1/0 = Not Defined = ∞
cot 30° = 1 / tan 30° = 1/(1/√3) = √3
cot 45° = 1 / tan 45° = 1/1 = 1
cot 60° = 1 / tan 60° = 1/√3
cot 90° = 1 / tan 90° = 1/∞ = 0
So, for a cot, it is
∞, √3, 1, 1/√3, 0
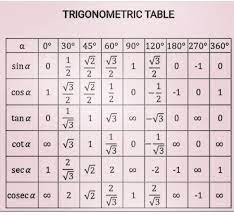
In Mathematics, these trigonometric tables are useful in a wide number of areas. Before we were introduced to pocket calculators, we had trigonometric tables with us. There are certain values in each trigonometric table that will help you to solve your sums and equations very easily. The trigonometric Table comprises sin, cos, tan, cosec, and sec values at different theta and here, theta is the value of the degree of angle.
If we talk about what this trigonometry is then, then trigonometry is the branch of mathematics that involves the study of relationships including that of the length of a triangle and its angles. Generally, trigonometry is associated with a right-angled triangle, a triangle in which one believes it lays at 90 degrees. It is not only used in solving mathematical problems, but it also has use in the field of navigation as well as other science and engineering fields.
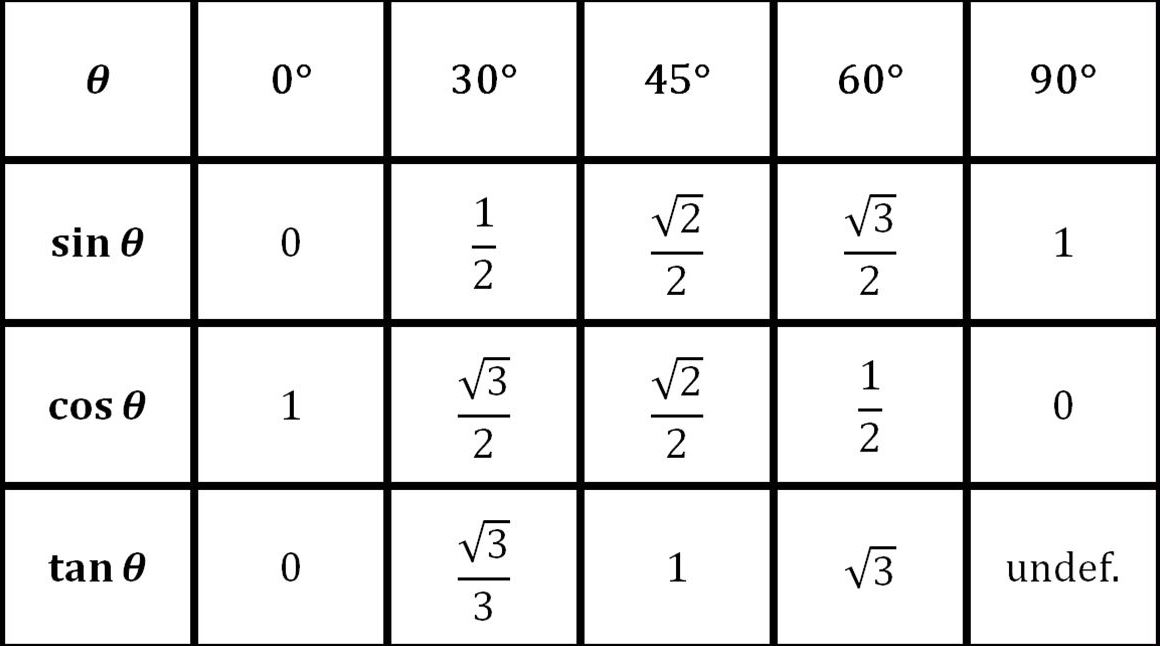
The trigonometry Table comprises the values of trigonometric ratios such as sine, Cosine, tangent, cotangent, cosecant, and secant from 0 to 360°. By applying values from 0 to 360°in these trigonometric ratios, we get the following values listed in the trigonometry value table:
 |
| trig table online |
 |
| trigonometry values table |
 |
| table of values trig |
 |
| trigonometry values table |
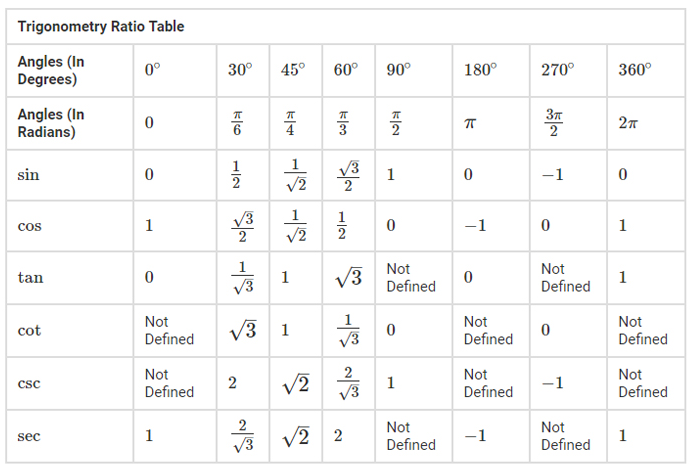
Here this table provides you with all the trigonometric values. This table is the base for you to solve a number of sums and equations with the trigonometric formula. It is often observed that many formulas are derived from these trigonometric values. This trigonometric table is basically the collection of all the trigonometric values but at different angles. 0° 30° 45° 60° and 90° are considered as the standard angles of trigonometric values.
tabel trigonometric
More about Trigonometric Table
We can see in the trigonometry value table the trigonometric ratios relate to each other, the variations occur in taking the different trigonometric ratios of sin, cosine, secant, cosecant, tangent, and cotangent.
trig chart
On-demand, the trigonometric functions are generated by calculators and modern computers also but by using special libraries of these mathematical codes. These trigonometric tables are going to make your work much easier. You just need to learn this table and most of the sums, and you will be able to solve them easily.
The trigonometric table is made up of the following trigonometric ratios that are interrelated to each other – sine, cosine, tangent, cosecant, secant, and cotangent. These ratios, in short, can be written as sin, cos, tan, cosec, sec, and cot.
The applications of Trigonometry in other associated scientific and mathematical fields are enormous with the distances on Earth as well as in space being estimated in the ancient world with the careful use and application of Trigonometry.
trigonometry value table
The calculations can easily be figured out by memorizing a table of functions most commonly known as the Trigonometric Table. This finds use in several areas. Some of them include navigation science, geography, engineering, geometry, etc. The trigonometric table was the reason for most digital development to take place at this rate today as the first mechanical computing devices found application through careful use of trigonometry.
exact values table
The Trigonometric ratios table gives us the values of standard trigonometric angles such as 0°, 30°, 45°, 60°, and 90°. These values hold increased precedence as compared to others as the most important problems employ these ratios. It is therefore very important to know and remember the ratios of these standard angles.
Memorizing the trigonometry table will be useful as it finds many applications, and there are many methods to remember the table. Knowing the Trigonometric Formulae automatically will lead to figuring out the table and the values. The Trigonometry ratio table is dependent upon the trigonometry formulas in the same way all the functions of trigonometry are interlinked with each other.
trigonometric values table
Trigonometric Functions
Now if we talk about what these trigonometric functions are, then these trigonometric functions are the functions of a right-angled triangle. These trigonometric functions are basically six in number and they're:
Sin function
Cos function
Tan function
Sec function
Cosec function
Cot function
These functions are basically the ones that are going to help you to solve the problems and get yourself clear with a number of concepts.
trig values table
Trigonometric Functions of Complementary Angles
Before attempting to begin, it is better to try and remember these values and know the following trigonometric formulae. Because if you are well aware of the formulas beforehand, then only it will be easy for you to attempt the questions. Every function is related to its corresponding function. Just as in the formulas below, you will observe that the sin function is related to the cos function and vice versa. Further, the is function is related to the tan function and vice versa. The other one which is sec function is also related to the cot function and vice versa.
trignometry table
sin x = cos (90°− x)
cos x = sin (90°− x)
tan x = cot (90°− x)
cot x = tan (90°− x)
sec x = cot (90°− x)
cot x = sec (90°− x)
1/sin x = 1/cos x = sin x
1/cos x = sec x
1/sec x = cos x
1/tan x = cot x
1/cot x = tan x
trigonometric tables trig tables sin cos angle table
table of values trig trigonometry table class 12
trigonometric identities class 12 trigonometric class 10
sinus and cosinus table class 12 pdf trigonometry formula
trignometry grade 10 trigonometry practice questions class 10
trig table online
ncert solutions for class 10 trigonometry
trignometric formulas class 12 all
class 12th trigonometry ratios table pdf
inverse trigo all formulae class 12
tips and tricks to solve trigonometry class 10
trigonometry table class 12 pdf
tan table of exact values
aeasy ways to memozie trig table
class 10 maths chapter 8 example 2,class 10 maths trigonometry
Tables of Trigonometric Function
When solving problems using trigonometric functions, either the angle is given and the value of t-function must be found, or the value of the t-function is given and angle must be found.
These two processes are inverse of each other. Thus inverse notations are used to express an angel in terms of the values of t-functions. For instant cos a = 0.5 can be put in the form a = cos -1 (-0.5) or a = Arc cos (- 0.5). The two expressions are read as Alpha equals to 'Inverse cos of (-0.5) or Alpha equals to Arc cos (- 0.5).
Both these operations can be done either using a calculator or using a trigonometric table. It should clearly be noted that both calculator or a table gives only approximate answers. Even so we use equality sign (=) but more correctly the use of approximation sign ( » ) is welcomed. Approximate values of the functions of acute angles are given in Tables of Natural Trigonometric functions. We shall use a Trigonometric table giving values to four decimal places. As it is clear that Tables cannot list all angles. Therefore, approximation must be used to find values between those given in the table. This method is known as Linear interpolation.
Assumption : Differences in functional values are directly proportional to the Differences in measures of angle over a very small interval.
Caution : This is not a real truth ! Yet it gives a better answer than just going for nearest value in the table.
Illustration 1
Using linear interpolation Find sin (240 43'), given that sin (240 40') = 0.4173 and sin (240 50') = 0.4200
Solution
We have sin (240 50') = 0.4200
and sin (24 0 40')= 0.4173
Difference for 10'= 0.0027
Owing to the assumption made if x is the difference for required 3' we have a ratio
\ x = 0.3 (0.0027) = 0.00081 » 0.0008 (rounded off to 4 decimal places)
Thus sin (240 40') = sin (24040') + sin (0.3') angle increase with an increment in its sine of angle and vice versa.
Thus sin (240 43') = 0.4173 + 0.0008 = 0. 4181
Illustration 2
Find cos (640 26'), given that cos (640 20') = 0.4331 and cos (640 30') = 0.4305
Solution
We have cos (640 30') = 0.4331
cos (640 20') = 0.4305
\ Tabular difference for 10' = 0.0026
\ The required difference for 6' = (If x)
\ x = 0.6 (0.0026) = 0.00156 or 0.0016 (104 decimal places)
As the angle increases, the cosine of angle decreases. Thus cos (640 26') = 0.4331 - 0.0016
= 0.4315.
Illustration 3
Find tan (28.43)0, given that tan (28.40)0 = 0.5407 and tan (28.50)0 = 0.5430
Solution
=
As angle increases, the tangent of angle also increases.
Thus tan (28.43)0 = 0.5407 + 0.0007 = 0.5414
Illustration 4
Solve the right triangle in which a = 24.36 Ð A = 58053'.
Solution
In right triangle ABC
A + B + C = 1800
\ 58053' + B + C = 180 0, given that C = 900
\ B = 90 0 - 58053' = 310 7'
Using the formulas for t-ratios,
b / a = cot A, b = a cot A = 24.36 (0.6036) = 14.70 (\ cot A = 0.6036)
c/a = csc A, c = a csc A = 24.36 (1.1681) = 28.45
a/c = sin A, c = a / sin A = 24.36 / 0.8562 = 28.45
b/c = cos A, b = c cos A = 28.45 (0.5168) = 14.70
Note : To save time, consider Illustration 1
Step (1) sin (240 41') = 0.4173, take only 4173
(2) Find mentally the tabular difference 27 between 4200 (for sin 240 40') and 4173 (for sin 240 40')
(3) Difference for 3' = 0.3 (27) = 8.1 (rounded off).
(4) Add (since sine) to 4178 to get 4181 then sin 240 31' = 0.4181.
Illustration 5
Find angle A, given that sin A = 0.4234
Solution
We will not find this entry in the table.
However 0.4226 = sin 250 0'
0.4253 = sin 250 10'
Tabular difference = 0.0027
Now 0.4226 = sin 25.0'
0.4234 = sin A
0.0008 = partial difference
correction = (nearest minute)
Adding (since sine) the correction is A = 250 0' + 3' = 250 3'
Illustration 6
Find A, given that cot A = 0.6345
Solution
We have 0.6330 = cot 570 40' (from the table)
0.6371 = cot 570 30'
Tabular diff. = 0.0041
Now 0.6330 = cot 570 40'
0.6345 = cot A
Partial diff. = 0.0015
Correction = (nearest minute)
subtracting (since cot), the correction is A = 570 40' - 4' = 570 36'.
Note : Saving the time as - (Consider Illustration 5)
Step (1) Locate the next smaller entry, 0.4226 = sin 250 0'. Use 4226 only.
(2) Find tabular diff. (mentally), 27.
(3) Find partial diff. (mentally), 8 between 4226 and 4234.
(4) Find (10') = 3' and add (since sine) to get A = 250 3'
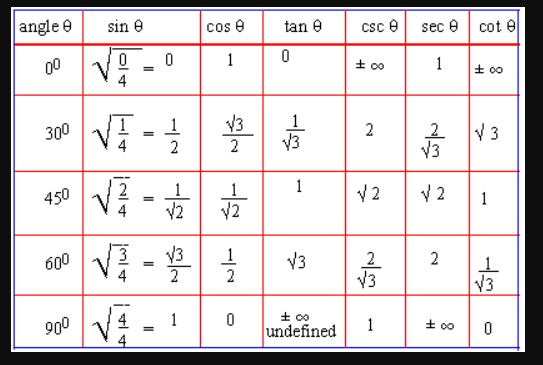
Commit to memory the values of t-functions of angles measuring 00, 300 , 450, 600 and 90 0as follows:
(1) Write angle (q) in the given order in the 1st column and the t-ratios, sin q, cos q, tan q, csc q, sec q, cot q in the 1st row.
(2) Put 0, 1, 2, 3, 4 in sin q column (see the table), then put 4, 3, 2, 1, 0 in cos q column (see the table).
(3) Divide by 4 to each entry then find square root of each entry. These are values of sine and cosine ratios of angles 00, 300, 450, 60 0and 900
(4) Use tan q = q and reciprocal relations for csc q, sec q and cot q.














0 Comments